Escape Room #
Guide #
🤠 Each locked room will provide you with hints and clues. Follow these clues to figure out each room’s key, and add it onto the url to pass to the next room.
pseudocode/pseudo_escape/key
🤠 Your only tools are this Guide and your loyal pseudocode compiler. No paper or digital calculations/conversions will be accepted.
🤠 When you escape a room, DO NOT SHARE THE ESCAPE KEY WITH YOUR COMPATRIOTS. You may share strategies and help them debug only.
🤠 After escaping each room, paste the working pseudocode which outputs the correct solution into your lab log.
🤠 Use the tips below to help you solve each of the riddles. They are listed in order from smallest to biggest hints. The bottom hint will give you the direct steps to solve the riddle, so that you don’t get stuck.
Useful Advice #
Alphabet #
You may find this useful on your journey
ALPHABET = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
Indexing Strings #
You can index into strings the same way you would into an array:
TEXT = "howdy pardner"
output TEXT[0]
output:
h
Modulo #
Remember, modulo will give you the remainder of devision.
NUM = 5 mod 2
>>> 1
Let’s Go! #
🏜🐄🌵 Are you ready to begin?Click here to start your adventure
🏜🐄🌵
Hints #
Room #1 #
Room #2 #
Room #3 #
Extension - Past Exam Question #
A program is developed to simulate the roll of dice in a game.
Three dice are thrown, with faces that have numbers from 1 to 6.
The dice are thrown seven times, and the data are stored in a two-dimensional array called DICEDIAL (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: The example data stored in the DICEDIAL array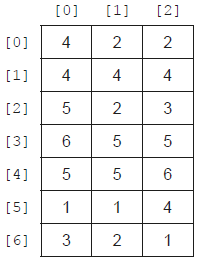
(a) 💻 Construct an algorithm in pseudocode to calculate the sum of all values stored in the DICEDIAL array.
#
The sub-program DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,R) checks whether there are repeated numbers in row R. If the numbers are not repeated, it returns 0, otherwise it returns the repeated number.
The DuplicateNum() sub-program will produce the following from the values used in Figure 2:
DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,0) returns 2DuplicateNum (DICEDIAL,1) returns 4DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,2) returns 0
(b) 💻 Construct an algorithm in pseudocode for the sub-program DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,R).
#
The sub-program highestRT(DICEDIAL) accepts the DICEDIAL array and outputs the highest row total and the indexes of all the rows with that total.
From the example data given in Figure 2, highestRT(DICEDIAL) would output that the highest row total is 16, and it occurs in the rows with indexes 3 and 4.