Computer Organization
# Topic 2 Revision from Computer Science Cafe.
Topic 2 Key Terminology from Computer Science Cafe.
Topic 2 Quizlet Flashcards from CS Classroom.
Topic 2 Video from CS Classroom.
Key Terms
# View Hardware/OS Terms
↕
Term Meaning Central processing unit (CPU) The part of a computer that performs the majority of the processing and calculation tasks. Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) The part of the CPU responsible for performing arithmetic and logical operations. Control unit (CU) The part of the CPU responsible for coordinating and controlling the other components of the CPU. Registers Small areas of memory within the CPU used to store and manipulate data quickly. Data bus The communication pathway between the CPU and other components that transfers data. Address bus The communication pathway between the CPU and other components that carries memory addresses. Primary memory The main memory used by a computer to store data and program instructions that are currently being used. Random access memory (RAM) A type of primary memory that is volatile and can be read from and written to by the CPU. Read-only memory (ROM) A type of primary memory that is non-volatile and contains instructions that cannot be altered. Cache memory A small amount of high-speed memory used to store frequently accessed data for faster access by the CPU. Machine instruction cycle The process of fetching, decoding, executing, and storing machine instructions within the CPU. Secondary memory Long-term storage used to store data and programs that are not currently being used. Volatile Memory that loses its contents when power is removed. Non-volatile Memory that retains its contents even when power is removed. Operating system Software that manages the resources and activities of a computer, and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. Application software Software designed for specific tasks or purposes, such as word processing, spreadsheets, or graphic design. Graphical user interface (GUI) A user interface that allows users to interact with a computer using graphical elements, such as icons, windows, and menus.
View Data Representation Terms
↕
Term Meaning Binary representation A method of representing data using only two digits, 0 and 1. Bit A single unit of binary data, either 0 or 1. Byte A group of 8 bits, used to represent a larger unit of data. Boolean operators Logical operators used to combine or manipulate binary data, including AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, and XOR. Truth tables Tables used to represent the outputs of Boolean expressions for every possible combination of inputs. Logic gates Electronic components used to implement Boolean expressions and perform logical operations. Denary/Decimal A base-10 numbering system, used to represent decimal numbers. Hexadecimal A base-16 numbering system, used to represent binary data more efficiently. Logic diagrams Diagrams that use logic gates and Boolean expressions to represent and solve problems. AND A Boolean operator that returns true if and only if both of its inputs are true. OR A Boolean operator that returns true if at least one of its inputs is true. NOT A Boolean operator that negates the input, returning true if the input is false, and vice versa. NAND A Boolean operator that returns false if and only if both of its inputs are true. NOR A Boolean operator that returns true if both of its inputs are false. XOR A Boolean operator that returns true if and only if exactly one of its inputs is true. String A sequence of characters used to represent text in a computer program. Integer A whole number used to represent numerical values in a computer program. Characters Single letters, digits, symbols, or other marks used in a computer program. Unicode A character encoding standard that allows computers to represent and manipulate text from different writing systems. Ergonomics The study of designing equipment and devices that are comfortable and efficient for human use. Accessibility The degree to which a system or device can be used by people with disabilities or special needs. Thinking logically A problem-solving approach that involves breaking down problems into smaller parts and using reasoning to arrive at solutions. Connecting computational thinking and program design The process of using computational thinking principles to design effective and efficient programs.
Example Problems
# State the hexadecimal equivalent of the following binary number: 11011111. [1]
State the hexadecimal equivalent of the binary number 11111011. [1]
State the hexadecimal representation of the binary number 10001010. [1]
State the hexadecimal equivalent of the binary number 10011110. [1]
Calculate the denary (base 10) equivalent of the hexadecimal number BF. [2]
State the binary equivalent of the denary number 89. [1]
State the binary equivalent of the denary number 37. [1]
Calculate, showing your working in each case: the binary (base 2) value of the denary (base 10) number: 105. [2]
Calculate, showing your working in each case: the hexadecimal (base 16) value of the denary (base 10) number: 200. [2]
Each pixel on a computer screen has three colour values associated with it: red, green and blue. The range for each of the three colour values is from 0(10) to 255(10). Colour values can also be represented in hexadecimal. For example, the colour blue can be represented in hexadecimal as 0000FF.
(a) State the binary representation of the colour blue. [1]
(b) State the number of colours that can be represented in each pixel on the computer screen. [1]
Colours are represented by a computer as a combination of the three primary colours: red, green and blue. Numerical values are used to represent the different shades of each primary colour. These values range from 0 to 255 in decimal, or 00 to FF in hexadecimal.
(a) State why hexadecimal numbers are frequently used in computing. [1]
(b) State the number of bits used to represent a non-primary colour, such as yellow. [1]
(c) State the maximum number of colours that can be represented in a computer pixel. [1]
Outline one reason for using Unicode to represent data in a computer system. [2]
Answer
↕
Award [2 max]: Unicode is an established standard for data representation, providing a single encoding scheme for all languages and characters. It allows data to be used and transported through many different systems, platforms, and devices. Unlike ASCII, which uses 8 bits, Unicode uses 16 or 32 bits, enabling it to represent over a million characters. Unicode supports a wide range of characters, including those from over 150 modern and historic scripts, as well as emoji. It offers different character encodings such as UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32, ensuring compatibility and flexibility across various applications. Boolean operators
# Define the NOR Boolean operator. [1]
Define the Boolean operator XOR. [2]
Define the Boolean NAND operator. [1]
Logic Gates and Circuits
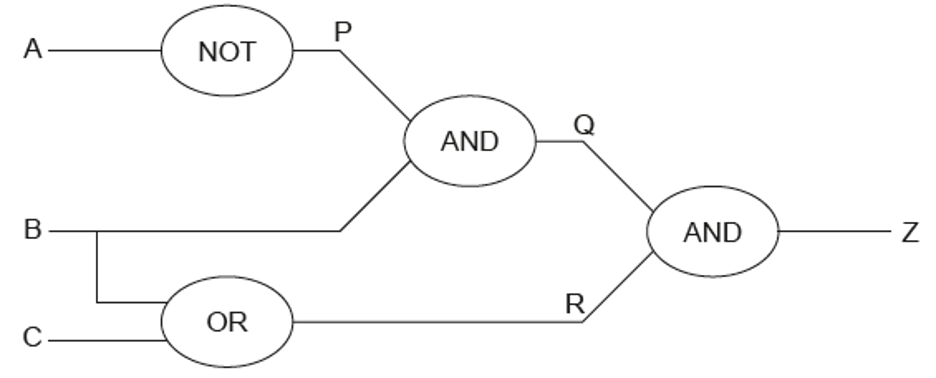
# A car has features that monitor its speed, direction and distance from the car in front.
Input Binary representation Description A 0 Car is less than 20 metres from the vehicle in front. A 1 Car is 20 metres or more from the vehicle in front. B 0 Car is travelling in reverse or stationary. B 1 Car is travelling forward. C 0 Car speed is more than 130 kilometres per hour. C 1 Car speed is 0-130 kilometres per hour.
For example, if the car is travelling forward, input B would have a binary representation of 1.
(a) Construct a logic diagram with inputs A, B, and C and output Z to represent the following scenario:
Output Z equals 1 when:
The car is travelling forward AND it is less than 20 metres from the vehicle in front. OR The car speed is more than 130 km per hour. In all other conditions, output Z equals 0. [4]
Answer
↕
Award [4 max]:
Answer should represent Z = A’.B + C’
Example answer:
Alternative answer:
Information similar to that presented in the chart above could be used to construct decisions and conditions in program design.
Identifier Description F Distance in metres to the vehicle in front S Speed of car in kilometres per hour T Travelling in a forward direction
(b) Determine the value of the following expression given that the input values for F, S and T are:
F = 5 S = 30 T = true
F >= 25 AND S >= 10 AND S <= 130 AND T = true [2]
You must show your working.
Answer
↕
Award [2 max]:
Award [1] for evidence of working e.g. substitution into variables to evaluate the expression. Award [1] for correct answer false. Example answer:
5 >= 25 AND 30 >= 10 AND 30 <= 130 AND true
false AND true AND true AND true
( Output =) false
Note:
Accept 1/0 instead of True/False. Truth Tables
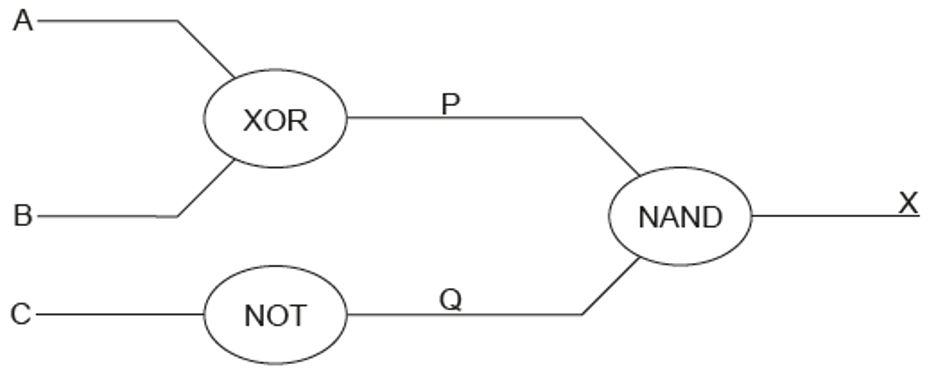
# Construct a truth table for the logic expression A NAND (B NOR C). [4]
Construct a truth table for the following expression: A OR NOT B AND C. [3]
Copy and complete the following truth table where:
X = A XOR B Y = A NOR C Z = X OR NOT Y [4]
Answer
↕
Award [4 max]:
Award [1] for all 8 input values correct. Award [1] for correct X column. Award [1] for correct Y column. Award [1] for correct Z column. Allow follow through from incorrect columns X or Y.
A B C X Y Z 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
Construct a truth table for the logic expression (A NAND B) NOR C. [4]
Construct a truth table for the following logical expression: (A XOR B) AND NOT C. [4]
Construct a truth table for the following expression: (A XOR B) AND B. [3]
Answer
↕
Award [3 max]:
Award [1] for all four combinations of two inputs. Award [1] for 3 correct outputs. Award [1] for all 4 correct outputs. Example:
A B (A XOR B) AND B 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Construct the truth table for the following logic circuit. [4]
Construct the truth table from the following logic circuit. [3]
Draw the truth table for the following logic circuit. [4]
Draw the logic circuit represented by the following truth table. [2]
Answer
↕
Award [2 max]:
Example 1:
Correct inputs and XOR gate; NOT gate, correct final output and link from XOR gate; Example 2:
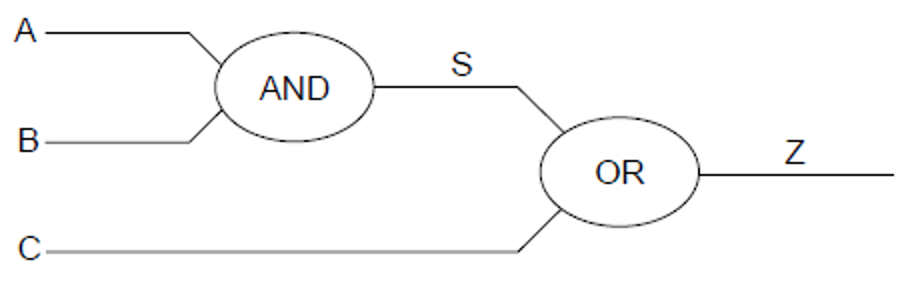
2 marks, 1 mark for each correct input in OR gate. Note: In this example, the two inputs in the OR gate are (NOT A AND NOT B) and (A AND B). 1 mark for drawing any 3 gates (complete with inputs and outputs). Construct a logic diagram for the following expression: [3]
NOT A OR (A AND B).
Computer Architecture
# Outline the purpose of the memory data register (MDR). [2]
Outline the purpose of the memory address register (MAR). [2]
Outline the purpose of the memory address register (MAR) in the central processing unit (CPU). [2]
Identify three functions of the control unit (CU) in the central processing unit (CPU). [3]
Markscheme
↕
Award [3 max]:
Fetches/extracts each instruction from memory; Decodes/transforms them into several commands/signals/steps (that are passed to the ALU or I/O or other components in the CPU for execution); Controls the movements of data within the CPU; Generates the clock pulses that regulate the speed of the instruction cycle; Generates control signals for all hardware components to regulate their activities; Synchronizes all the operations of the CPU; Note: Accept other reasonable answers.
State the function of the control unit (CU) in the central processing unit (CPU). [1]
Explain the purpose of cache memory. [3]
State the part of the central processing unit (CPU) that is responsible for carrying out calculations. [1]
Distinguish between two types of primary memory. [2]
Markscheme
↕
Award [2 max]:
RAM is a volatile/temporary memory (which could store the data as long as the power is supplied) and ROM is a permanent/non-volatile memory (which could retain the data even when power is turned off); Data stored in RAM can be altered whilst data stored in ROM can only be read; RAM is used to store the instructions/data/programs that are currently being processed/in use whereas ROM is used to store permanent data/files such as start-up instructions for the computer; RAM - large physical chip size/higher capacity/expensive whilst ROM - small size/less capacity/cheaper; The CPU can access the data stored in RAM directly whilst the CPU cannot access the data stored on ROM (unless the data is stored in RAM). Note: Do not award marks for Cache memory.
Identify one characteristic of random access memory (RAM). [1]
Explain the use of cache memory. [3]
Distinguish between random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). [2]
Explain how cache memory affects system performance. [3]
The machine instruction cycle is a sequence of actions that a central processing unit (CPU) performs to execute each machine code instruction in a program.
(a) State where the program is held. [1]
(b) State the part of the central processing unit (CPU) that performs the decoding. [1]
(c) Outline the function of the memory address register (MAR). [2]
Operating Systems and Applications
# Identify one function of a single-user operating system. [1]
Markscheme
↕
Award [1 max]:
Note: Allow any other correct function of a single-user operating system.
Outline the function of a web browser. [2]
State two features of a web browser. [2]