Abstract Data Structures
# Topic 5 Revision from Computer Science Cafe.
Topic 5 Key Terminology from Computer Science Cafe.
Video 1 from CS Classroom (Intro, 2D Arrays, Recursion)
Video 2 from CS Classroom (Stacks and Queues)
Key Terms (covered)
# Example Problems Stacks + Queues
# 1. Identify two applications of a stack. [2]
2. Identify two applications of queues in computing. [2]
Answer
↕
Award [2 max]:
Print queue (serving requests on a shared printer) / spooling in printer. CPU task scheduling. Handling of interrupts (in the same order as they arrive). Buffer for devices like keyboard. Queues in routers / switches. Mail queues. Simulation / computer modeling of physical queues (e.g., a customer waiting line in a supermarket queue, a call center where technical personnel take calls and provide service, etc.). Handling website traffic / network congestion. Maintaining playlist in media player. Note: Accept other appropriate examples of applications of queues in computing.
3. Stack operations. [6]
A stack is a data structure that is used in the implementation of a recursive method.
(b) Outline the purpose of the stack access method isEmpty(). [2]
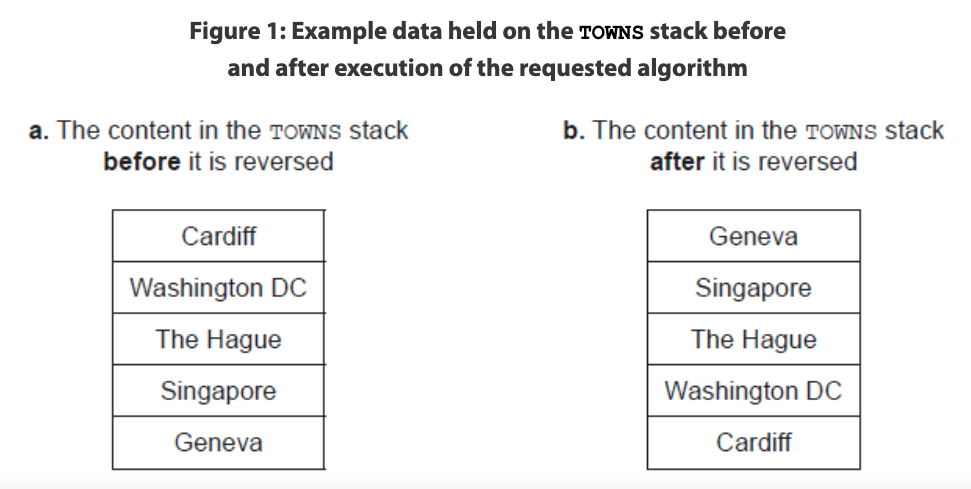
# The stack TOWNS holds several town names, and the name “Cardiff”is on the top of
the TOWNS stack (see Figure 1a).
An algorithm is needed that will reverse the contents of the TOWNS stack. The name
“Geneva” should be on top of the TOWNS stack after reversing its contents (see
Figure 1b).
(c) Construct an algorithm that will reverse the TOWNS stack using an empty queue. [5]
# Answer
↕
Award [5 max]:
Award [1] for correct use of stack and queue access methods (isEmpty(), push(), pop(), enqueue(), dequeue()). Award [1] for looping through the TOWNS stack. Award [1] for taking an element from the top of the TOWNS stack. Award [1] for enqueuing the value popped from the TOWNS stack to the TEMP queue. Award [1] for looping through the TEMP queue and pushing the dequeued value back onto the TOWNS stack. Example:
loop while not TOWNS . isEmpty ()
X = TOWNS . pop ()
TEMP . enqueue ( X ) // TEMP is an empty queue
end loop
loop while not TEMP . isEmpty ()
Y = TEMP . dequeue ()
TOWNS . push ( Y )
end loop
4. A computer science student is coding and running a program while several documents, such as essays, lab reports and homework, are being printed out.
(a) Define the term queue as a data structure. [1]
# (b) Identify two different queues used in the given scenario. [2]
# Answer
↕
Award [2 max]:
Print queue. Keyboard queue. Accept any other job queue (e.g., program is running).
5. Identify one characteristic of a queue. [1]
Example Problems 2D Arrays
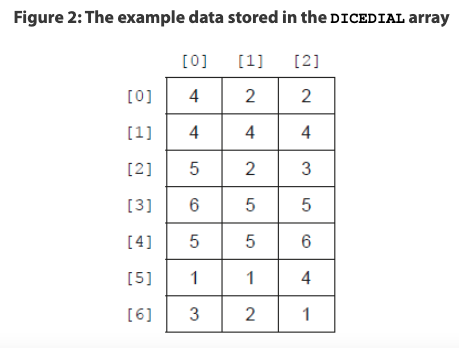
# 1. 2D Arrays using dice rolls. [15]
A program is developed to simulate the roll of dice in a game.
Three dice are thrown, with faces that have numbers from 1 to 6.
The dice are thrown seven times, and the data are stored in a two-dimensional array called DICEDIAL (see Figure 2).
(a) Construct an algorithm in pseudocode to calculate the sum of all values stored in the DICEDIAL array. [3]
# Answer
↕
Award [3 max]:
Award [1] for a correct row loop. Award [1] for a correct column loop. Award [1] for initializing SUM and summing inside the loop using correct array indexes. Example 1:
SUM = 0
loop I from 0 to 6
// accept DICEDIAL . length - 1
// or len ( DICEDIAL ) - 1 instead of 6
loop J from 0 to 2
// accept DICEDIAL [ I ] . length - 1
// or len ( DICEDIAL [ I ]) - 1 instead of 2
SUM = SUM + DICEDIAL [ I ][ J ]
end loop
end loop
Example 2:
I = 0
SUM = 0
loop while I <= 6
j = 0
loop while J <= 2
SUM = SUM + DICEDIAL [ I ][ J ]
J = J + 1
end loop
I = I + 1
end loop
The sub-program DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,R) checks whether there are repeated numbers in row R. If the numbers are not repeated, it returns 0, otherwise it returns the repeated number.
The DuplicateNum() sub-program will produce the following from the values used in Figure 2:
DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,0) returns 2
DuplicateNum (DICEDIAL,1) returns 4
DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL,2) returns 0
(b) Construct an algorithm in pseudocode for the sub-program DuplicateNum(DICEDIAL, R). [4]
# Answer
↕
Award [4 max]:
Example 1 (if-else statement):
Award [1] for initializing VAL to 0 and returning VAL (in case no duplicates). Award [3 max] for determining a correct value (1 mark for each correct condition and change of the value of VAL if needed). Note: Award marks for determining a correct return value in each of possible cases: three different values in row R- no duplicates, any two numbers/values in row R are the same and all three values in row R are the same. Award [1] for correct use of row index and column index in the DICEDIAL array. Note: the method heading may not appear in a candidate’s response. DuplicateNum ( DICEDIAL , R )
VAL = 0
if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1]
VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0]
else if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0]
else if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1]
end if
return VAL
end DuplicateNum
Example 2 (several if statements- inefficient, but it outputs a correct value):
Award [1] for each correct if statement, ×4 Award [1] for correct use of row index and column index in the DICEDIAL array if // three different numbers
DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] != DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1]
and DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] != DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
and DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] != DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
then
RESULT = 0
end if
if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] and DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
then // three same numbers
RESULT = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0]
end if
// any two same
if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] or DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
then
RESULT = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0]
end if
if DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
then
RESULT = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1]
end if
return RESULT
Note: Accept answers written in Java/ Python. The following example answer is written in Java. public int DuplicateNum ( int [][] DiceDial , int row )
{
if ( DiceDial [ row ][ 0] == DiceDial [ row ][ 1] || DiceDial [ row ][ 0] ==
DiceDial [ row ][ 2])
{
return DiceDial [ row ][ 0];
}
else if ( DiceDial [ row ][ 1] == DiceDial [ row ][ 2])
{
return DiceDial [ row ][ 1];
}
else return 0;
}
Example 3 (single loop):
Award [1] for initializing VAL to 0 and return VAL Award [1] for correct loop Award [1] for correct condition and change of VAL Award [1] for if statement after the loop Award [1] for correct use of row index and column index in the DICEDIAL array DuplicateNum ( DICEDIAL , R )
VAL = 0
loop K from 0 to 1
if ( DICEDIAL [ R ][ K ] == DICEDIAL [ R ][ K + 1])
then
VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ K ] // or DICEDIAL [ R ][ K + 1]
end if
end loop // determines VAL
// comparing only DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] with DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1]
// and DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] with DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
if ( DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] == DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2])
then
VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] // or DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
end if
return VAL
end DuplicateNum
Example 4 (nested loops):
Award [1] for initializing VAL to 0 and return VAL Award [1] for correct outer loop Award [1] for correct inner loop Award [1] for correct condition and change of VAL Award [1] for correct use of indexes in the DICEDIAL array VAL = 0
loop K from 0 to 1
loop J from K + 1 to 2
if DICEDIAL [ R ][ K ] == DICEDIAL [ R ][ J ]
then VAL = DICEDIAL [ R ][ K ]
end if
end loop
end loop
return VAL
The sub-program highestRT(DICEDIAL) accepts the DICEDIAL array and outputs the highest row total and the indexes of all the rows with that total.
From the example data given in Figure 2, highestRT(DICEDIAL) would output that the highest row total is 16, and it occurs in the rows with indexes 3 and 4.
(c) Construct an algorithm in pseudocode for the sub-program highestRT(DICEDIAL). [8]
# Answer
↕
Example 1:
Award [8 max]:
Award [1] for initializing HIGHEST. Award [1] for a correct row loop (I). Award [1] for calculating the sum of all elements in the Ith row. Award [1] for using correct indexes in the DICEDIAL array. Award [1] for comparing the row sum with the highest row sum so far. Award [1] for changing the value of HIGHEST if needed. Award [1] for outputting the highest row sum once. Award [1] for a second loop to output row numbers with the highest total. Example:
highestRT ( DICEDIAL )
HIGHEST = 0
loop I from 0 to 6
SUM = DICEDIAL [ I ][ 0] + DICEDIAL [ I ][ 1] + DICEDIAL [ I ][ 2]
if SUM > HIGHEST
HIGHEST = SUM
end if
end loop
output ( 'The highest row total:' , HIGHEST )
output ( 'The highest row total occurs in the following rows:' )
loop I from 0 to 6
SUM = DICEDIAL [ I ][ 0] + DICEDIAL [ I ][ 1] + DICEDIAL [ I ][ 2]
if SUM = HIGHEST
output ( I )
end if
end loop
end highestRT
Example 2:
Award [2 max] for defining the ROWTOTALS array (1 mark for correct row loop (I) and 1 mark for calculating the sum of all elements in the Ith row of the DICEDIAL array) Award [1] for initializing HIGHEST Award [3 max] for searching for the highest (1 mark for the correct loop, 1 mark for comparing the row sum with the highest row sum so far and 1 mark for and changing the value of HIGHEST if needed) Award [1] for outputting the highest row sum once Award [3 max] outputting the numbers of rows with the highest total (1 mark for a loop, 1 mark for comparing the row total with the highest total and 1 mark for outputting the corresponding index in the ROWTOTALS array) loop I from 0 to 6
S = 0
loop K from 0 to 2 S = S + DICEDIAL [ I ][ K ]
end loop
ROWTOTALS [ I ] = S
end loop
// ROWTOTALS [ R ] holds the sum of all
// numbers in row R of the DICEDIAL array
HIGHEST = 0 // any number <= 0 OR ROWTOTALS [ 0]
loop I from 0 to 6
if ROWTOTALS [ I ] > HIGHEST
then HIGHEST = ROWTOTALS [ I ]
end if
end loop // searching for the highest row total
output ( ‘ the highest row total : ’ , HIGHEST )
output ( ‘ the highest row total occurs in the following rows : ’ )
loop I from 0 to 6
if ROWTOTALS [ I ] = HIGHEST
then output ( I )
end if
end loop
Example 3:
Award [1] for initializing MAXT Award [1] for correct row loop (R) Award [1] for calculating the sum of all elements in row R (using correct indexes in the DICEDIAL array) Award [1] for comparing the row sum with the highest row sum so far (S == MAXT), and changing
the value FLAGMAXTIND[R] to 1 if they are equal Award [1] for comparing the row sum with the highest row sum so far (S > MAXT) and updating the highest row sum so far Award [1] for reinitializing FLAGMAXTIND array Award [1] for changing the value FLAGMAXTIND[R] to 1 Award [1] for outputting the highest row total only once Award [2] for outputting row numbers with the highest total (1 mark for a loop, 1 mark for output within if statement) // assume FLAGMAXTIND - zero array initialized
MAXT = 0
loop R from 0 to 6
S = DICEDIAL [ R ][ 0] + DICEDIAL [ R ][ 1] + DICEDIAL [ R ][ 2]
if S = MAXT
then
FLAGMAXTIND [ R ] = 1
end if
if S > MAXT
then
MAXT = S
loop K from 0 to 6
FLAGMAXTIND [ K ] = 0
end loop
FLAGMAXTIND [ R ] = 1
end if
end loop
output ( 'The highest row total is' , MAXT )
output ( ' and it occurs in the following rows:' )
loop R from 0 to 6
if FLAGMAXTIND [ R ] == 1 // or FLAGMAXTIND [ R ] != 0
then
output ( R )
end if
end loop
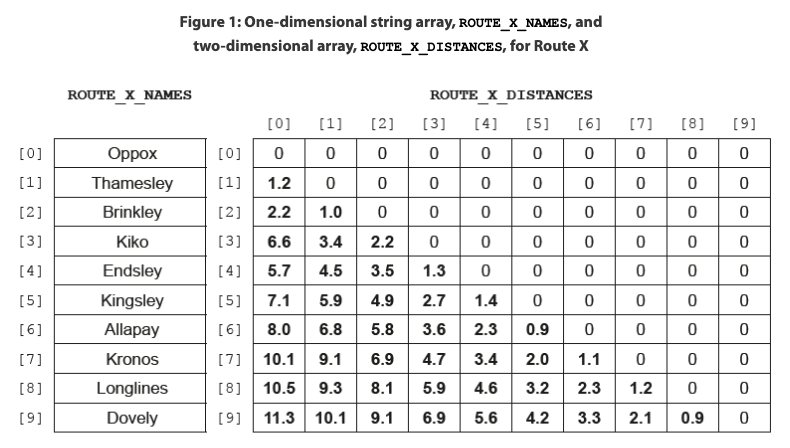
2. Bus Stops [15]
A bus company provides services within a city. Passengers can look up the distance between any two bus stations on any of its routes.
For each route, a one-dimensional string array is used to store the names of all bus stations on the route, and a two-dimensional array is used to store the distances between the bus stations (in kilometers). Only the lower triangle of the two-dimensional array is used to store the distances.
Figure 1 shows data about Route X, a bus route between Oppox and Dovely.
For example, the distance between Kingsley and Kronos (2.0 kilometers) can be found in ROUTE_X_DISTANCES[7][5].
(a) State the distance between Kiko and Longlines. [1]
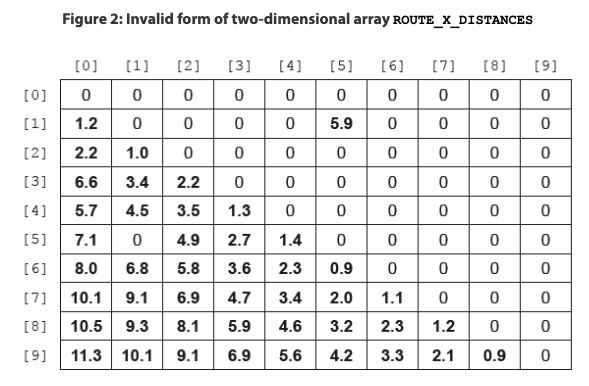
# The two-dimensional array ROUTE_X_DISTANCES is valid if all the entries on and above the main diagonal are zero and all the entries below the main diagonal are greater than zero.
(b) Construct an algorithm in pseudocode that checks the elements of the array ROUTE_X_DISTANCES and outputs whether the array is valid or not. [5]
# Note: Marks should also be awarded if a candidate wrote the algorithm in Java/Python/Javascript.
Answer
↕
Award [5 max]:
Award [1] for correct outer/row loop. Award [1] for correct inner/column loop. Award [1] for use of a flag. Award [1] for checking whether all elements on and above the main diagonal are zero. Award [1] for checking all elements below the main diagonal (they all should be positive numbers). Award [1] for outputting the appropriate message. Example 1 :
VALID = True
loop R from 0 to 9
loop C from 0 to 9
if R > C and ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ R ][ C ] <= 0
then VALID = False
end if
if R <= C and ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ R ][ C ] != 0
then VALID = False
end if
end loop
end loop
if VALID
then output ( 'VALID' )
else output ( 'INVALID' )
end if
Example 2 :
FLAG = 1
loop R from 1 to 9
loop C from 0 to R - 1
if ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ R ][ C ] <= 0
then FLAG = 0
end if
end loop
end loop
loop R from 0 to 9
loop C from R to 9
if ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ R ][ C ] != 0
then FLAG = 0
end if
end loop
end loop
if FLAG == 1
then output ( 'IT IS VALID' )
else output ( 'IT IS NOT VALID' )
end if
Note: Award marks if algorithm is presented in a Java/Python/Javascript/any other program rather than IB pseudocode.
For example, please see the following Javascript program
Answer
↕
Award [6 max]:
Award [1] for all variables correctly declared and initialized. Award [1] for looping through the array ROUTE_X_NAMES. Award [1] for determining positions of the first name in the array. Award [1] for determining positions of the second name in the array. Award [1] for outputting a message if one or the other is not present. Award [1] for a comparison of positions to find the largest. Award [1] for the correct output of distance from ROUTE_X_DISTANCES. Example 1 :
NAME1 = input ()
NAME2 = input ()
POS1 = - 1
POS2 = - 1
K = 0
loop while K <= 9 and ( POS1 == - 1 or POS2 == - 1)
if ROUTE_X_NAMES [ K ] . equals ( NAME1 ) // accept '==' instead
then POS1 = K
end if
if ROUTE_X_NAMES [ K ] . equals ( NAME2 )
then POS2 = K
end if
K = K + 1
end while
if POS1 == - 1 OR POS2 == - 1
then output ( 'stations are not found' )
else
if POS1 > POS2
then output ( ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ POS1 ][ POS2 ])
else output ( ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ POS2 ][ POS1 ])
end if
end if
Example 2 :
ST1 = input ()
ST2 = input ()
PS1 = - 1
PS2 = - 1
loop K from 0 to 9
if ROUTE_X_NAMES [ K ] == ST1
then PS1 = K
end if
if ROUTE_X_NAMES [ K ] == ST2
then PS2 = K
end if
end loop
if PS1 != - 1 AND PS2 != - 1
then if PS1 < PS2
then T = PS1
PS1 = PS2
PS2 = T
end if
output ( ROUTE_X_DISTANCES [ PS1 ][ PS2 ])
else
output ( 'stations not found' )
end if
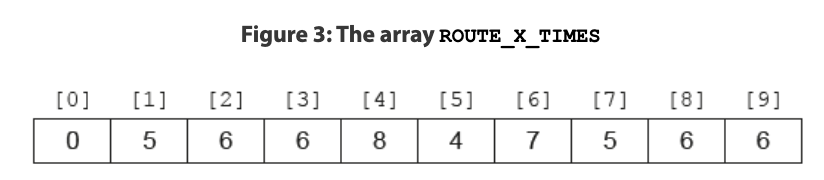
Explain how this data could be used to determine the number of minutes it takes for a bus to travel between any two bus stations. [3]
Example Problems Recursion
# Define the term recursion . [1]
Outline two disadvantages of recursive methods. [4]
Answer
↕
Award [4 max]
Memory intensive :
Recursion uses memory (call stack) to store all intermediate arguments and return values. This could lead to stack overflow if there is a large amount of data. Can be slow :
If not implemented correctly, recursion can result in too many recursive calls, slowing down execution. Complex logic :
Recursive functions can be difficult to construct, analyze, or understand due to the complexity of the paradigm. Consider the following recursive method:
def rec ( A ):
if A >= 2:
return rec ( A - 2) + rec ( A - 1)
else :
return 1
Determine the value of rec(5) (show all your working). [4]
# Answer
↕
Award [4 max]:
The working may be differently represented. If only the final result (8) is shown, then award only one mark.
rec ( 5)
= rec ( 3) + rec ( 4)
= rec ( 1) + rec ( 2) + rec ( 2) + rec ( 3)
= 1 + rec ( 0) + rec ( 1) + rec ( 0) + rec ( 1) + rec ( 1) + rec ( 2)
= 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + rec ( 0) + rec ( 1)
= 8
Explain how a stack may be used in the implementation of a recursive function. [4]
Consider the following recursive method:
fun ( N )
if N > 0
then
return ( N mod 10) + fun ( N div 10)
else
return 0
end if
end fun
(a) Determine the value of fun(1216). Show all your working. [4]
# Answer
↕
Award [4 max]:
The working may be differently represented. If only the final result (8) is shown, then award only one mark.
fun ( 1216) = 6 + fun ( 121);
= 6 + 1 + fun ( 12);
= 6+ 1+ 2+ fun ( 1);
= 6+ 1+ 2+ 1+ fun ( 0);
= 6+ 1+ 2+ 1+ 0= 10;
(b) Deduce the purpose of this recursive method. [2]
# Answer
↕
Award [2 max]:
Calculates/returns the sum;
Of all digits in N;
Key Terms (not covered)
# Not covered for Class of 2026
Term Meaning Heaps A tree-based data structure that is used to implement priority queues, where the highest priority element is always at the root. Linked lists A data structure that stores elements in nodes, where each node contains a value and a pointer to the next node. Double linked lists A linked list where each node has a pointer to both the next and the previous node. Circular linked lists A linked list where the last node points to the first node, creating a circular structure. Pointers A variable that stores the memory address of another variable. Binary trees A tree-based data structure where each node has at most two children. Non-binary trees A tree-based data structure where each node can have more than two children. Nodes An individual element of a data structure, such as a linked list or a tree. Parent node A node that has one or more children. Left-child node The child node of a parent that appears to the left. Right-child node The child node of a parent that appears to the right. Subtree node A smaller tree that is part of a larger tree. Root node The topmost node in a tree. Leaf node A node that has no children. Tree traversal The process of visiting all nodes in a tree data structure. Pre-order traversal A type of tree traversal where the root node is visited first, followed by the left subtree and then the right subtree. Post-order traversal A type of tree traversal where the left subtree is visited first, followed by the right subtree, and then the root node. In-order traversal A type of tree traversal where the left subtree is visited first, followed by the root node, and then the right subtree.