Shift Ciphers #
In this lab you will continue to practice functions and are introduced to modulo and file handling.
Syllabus Topics [SL] #
- B2.5.1 Construct code to perform file-processing operations.
Key Vocabulary #
| Word | Definition |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Converting plain text into a secure format, cipher text, that cannot be easily understood by unauthorized people. |
| Encryption Key | A string of characters or numbers used by an encryption algorithm to encode or decode data. |
| Modulo | An operation that returns the remainder of a division. |
| Path | Location of a file |
[0] Set up #
💻 Go to your
dpcs/unit01_cryptography folder.
cd ~/desktop/dpcs/unit01_cryptography/
💻 Clone your repo and go into the directory.
Be sure to replace yourGithubUsername with your actual username.
git clone https://github.com/isf-dp-cs/lab_shift_ciphers_yourGithubUsername
cd lab_shift_ciphers_yourGithubUsername
💻 Enter the Poetry Shell to start the lab. As a reminder, we will run this command at the start of each lab, but only when we are inside a lab folder.
poetry shell
👾 💬 Exiting the poetry shellWhen you want to exit the shell, you can type
exitor^D
[1] File Handling #
In this lab you will use file handling techniques to encrypt and decrypt large text files.
📖 To read a whole file
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
file.read()
file.close()
open()- opens a file in a specific mode, if the file does not exisit it creates a new file'example.txt'is the name of the file you want to open or create'r'represents the mode. important modes to remember are:'r'- read the text'w'- write over existing text'a'- append text to the end of the file
read()- returns all text in the fileclose()- closes the file
📖 To read a single line
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
file.readline()
file.close()
📖 To read a file line-by-line
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
for line in file:
print(line)
file.close()
📖 To add to an existing file
file = open('log.txt', 'a')
file.write('A new entry. \n')
file.close()
📖 To write to a new file
file = open('new_document.txt', 'w')
file.write('Hello world')
file.close()
💻 Open file_handling.py and construct code to perform the following actions.
- Open
song.txt, read the file, and print the text - Append the last line of the song. Be sure it is appended on the next line.
- last line:
You're my soda pop, gotta drink every drop
- last line:
- Create a new file
capitalized_song.txtwith lyrics of the song in all capital letters
[2] Modulo #
Python has many operators that allow you to perform calculations with values. You’ve probably
seen and used the basic ones like +(add), - (subtract), * (multiply), and / (divide).
However, Python has other operators that can be really helpful.
One such operator is the modulo operator (%). This operator takes two values, divides them, and returns the remainder of the division.
For example:
5/2 has a remainder of 1
5%2= 1
Here are some more modulo examples:
print(5%2)
>> 1
print(3%3)
>> 0
print(6%2)
>> 0
print(9%2)
>> 1
print(3%4)
>> 3
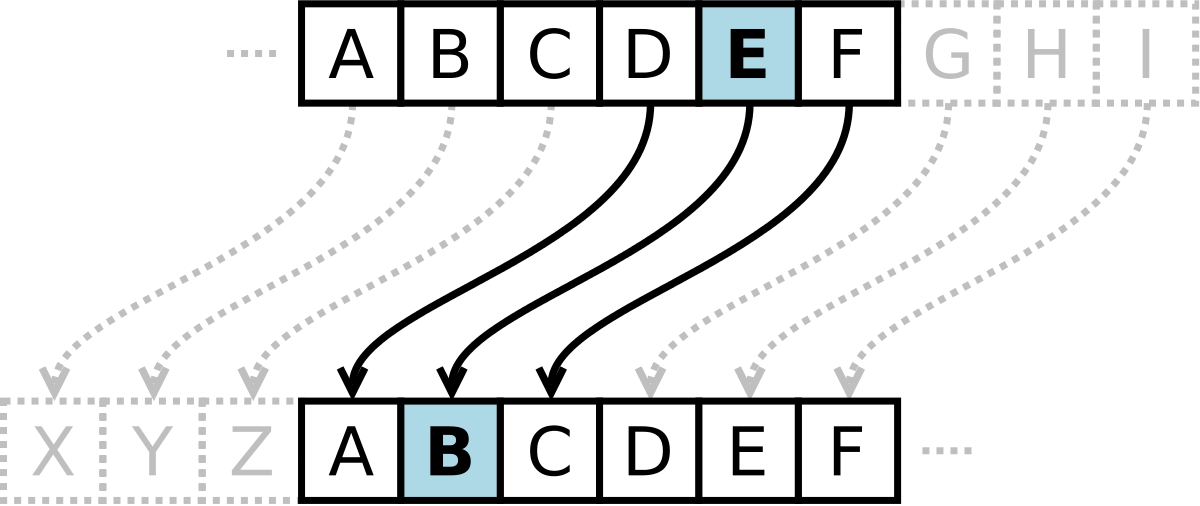
[3] Caesar Cipher #
The caesar cipher is a type of substitution cipher used by ancient Romans. It takes a message, the plain text and transforms it by shifting each letter by a set value, the encryption key.
For example imagine that the alphabet is shifted by 3.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | A | B | C |
The plain text "beg" with the encryption key 3, becomes "ehj".
bshifts by 3, becomingeeshifts by 3, becominghgshifts by 3, becomingj
💻 In caesar_cipher.py, construct the function decrypt_caesar_cipher() to decrypt a message that has been encrypted by a caesar cipher.
💻 Test your decryption function decrypt_caesar_cipher() on words and short phrases.
💻 Use your decrypt_caesar_cipher() function and file handling methods to decrypt the message in caesar_encrypted_text.txt. You should then create a new file with the decrypted text.
✅ Check your work by opening the created file and ensuring it makes sense as English text. Do you recogonize the text?
[4] Vigenere Cipher #
The Vigenere cipher is another substitution cipher. It takes a message, the plain text and transforms it by shifting each letter by a set value according to a repeating encryption key. Unlike the caesar cipher, the encryption key is a string.
For example, imagine that encryption key is 'be'.
| b | e |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5 |
'b' is number 1 in the alphabet and 'e' is number 5.
Therefore, we will shift our letters by 1 and 5, in an alternating pattern. For example the plain text "apple" with the encryption key "be", becomes "buqpf".
| a->b | shift by 1 |
|---|---|
| p->u | shift by 5 |
| p->q | shift by 1 |
| l->q | shift by 5 |
| e->f | shift by 1 |
💻 In vigenere_cipher.py, construct the function decrypt_vigenere_cipher() to decrypt a message that has been encrypted by a vigenere cipher.
💻 Test your decryption function decrypt_vigenere_cipher() on words and short phrases
💻 Use your decrypt_vigenere_cipher() function and file handling methods to decrypt the message in "vigenere_encrypted_text.txt". The encryption key is the encryption key from the caesar_cipher problem written in English (e.g. 1 is one). You should then create a new file with the decrypted text.
✅ Check your work by opening the created file and ensuring it makes sense as English text. Do you recogonize the text?
[5] Deliverables #
⚡✨ Once you complete the lab, be sure to complete these two steps:✏️ Go to your Syllabus Content Checklist in your Google Drive and update it accordingly.
💻 Push your work to Github
- git status
- git add -A
- git status
- git commit -m "describe your code here"
- git push
- git remote