Recursion #
In this lab you will apply the concept of recursion to two classic applications - traversing nested file folders and creating fractal images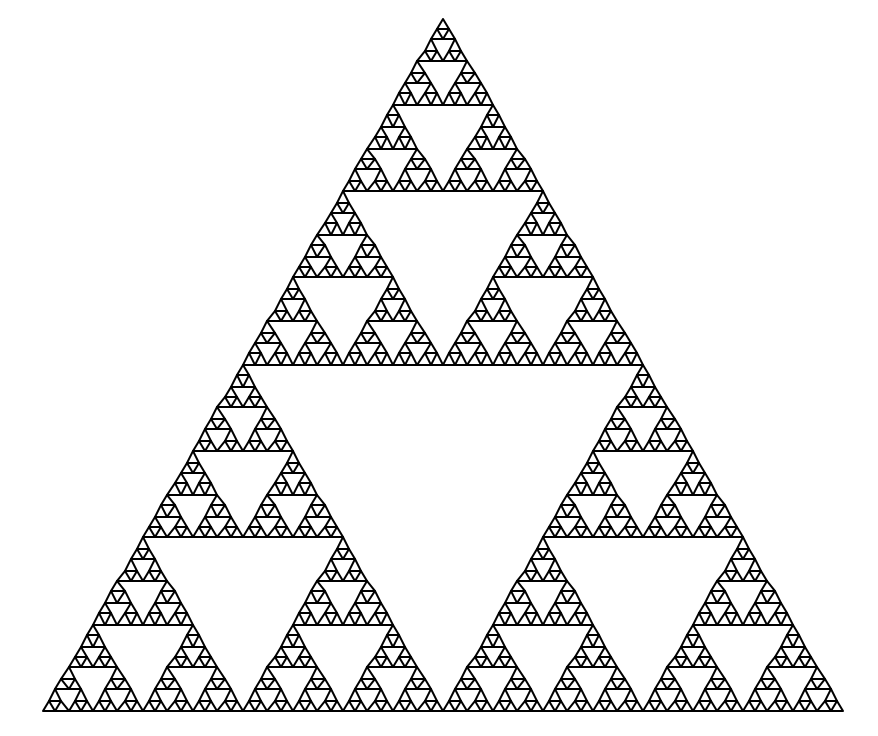
Syllabus Topics [HL] #
- B2.4.4 Explain the fundamental concept of recursion and its applications in programming. (HL only).
- B2.4.5 Construct and trace recursive algorithms in a programming language. (HL only)
Key Vocabulary #
| Word | Definition |
|---|---|
| Recursive Function | A function that calls on itself. |
| Recursive Case | The step where the function calls itself with a smaller subproblem. The recursive case must eventually lead to the base case to ensure the recursion terminates. |
| Base Case | The condition that stops the recursion. Without a base case, the recursion would continue infinitely, leading to a stack overflow error. |
| Stack Overflow | Each recursive call adds a new frame to the call stack. Excessive recursion can exhaust the stack memory, leading to stack overflow errors and crashing the program. |
[0] Set up #
💻 Go to your
dpcs/unit01_cryptography folder.
cd ~/desktop/dpcs/unit01_cryptography/
💻 Clone your repo and go into the directory.
Be sure to replace yourgithubusername with your actual username.
git clone https://github.com/isf-dp-cs/lab_recursive_drawing_yourgithubusername
cd lab_recursive_drawing_yourgithubusername
💻 Install Tkinter. We’ll need this for our drawings.
brew install python-tk
💻 Enter the Poetry Shell to start the lab. As a reminder, we will run this command at the start of each lab, but only when we are inside a lab folder.
poetry shell
👾 💬 Exiting the poetry shellWhen you want to exit the shell, you can type
exitor^D
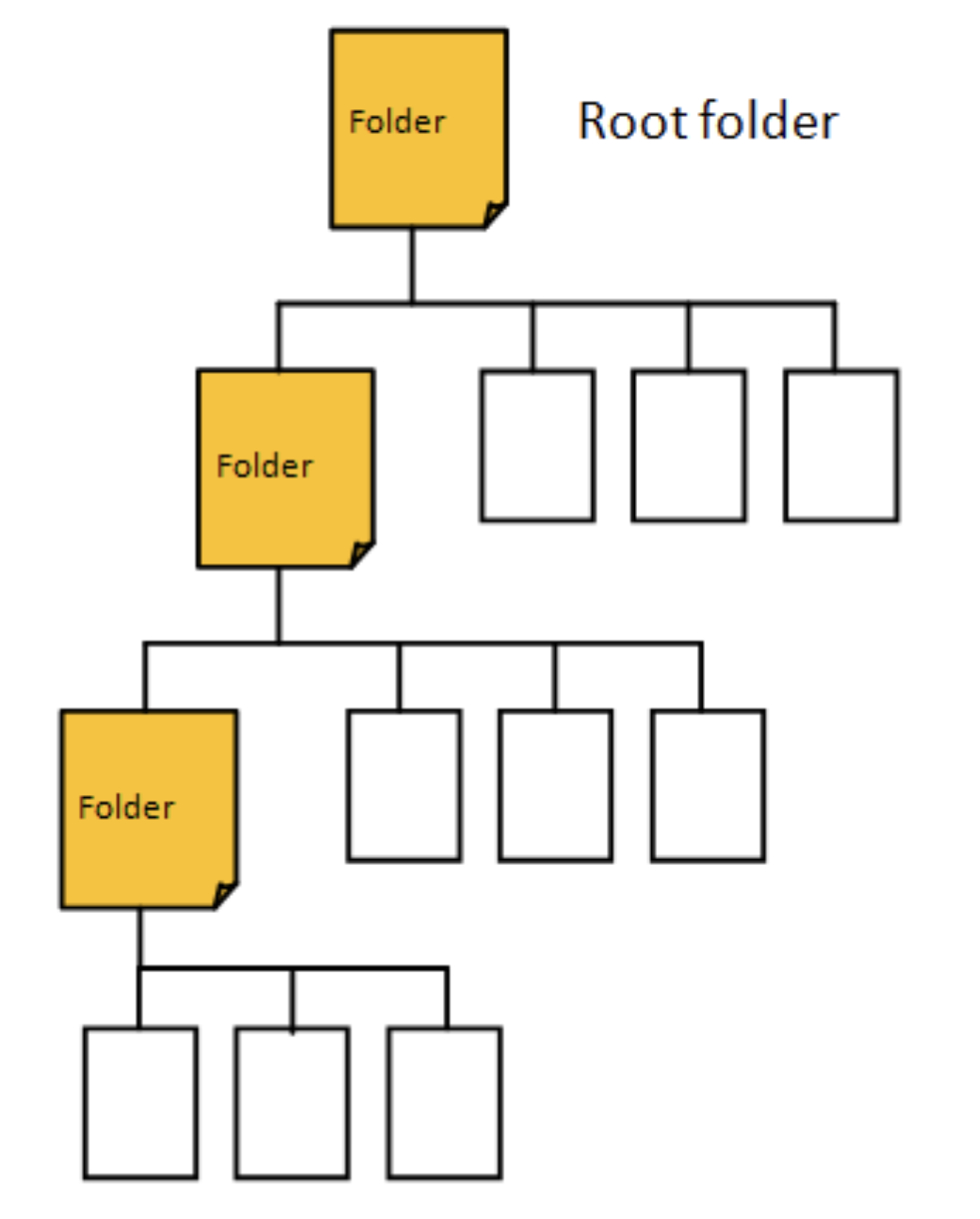
[1] Folders Structure #
Recursion can be helpful for searching through the file system of your computer.
OS Module #
In order to search through your files, you’ll need to utilize the Python OS Module. Most of the functions you need are included in the starter code, but you will also need these important two:
📖 Important OS functions
os.path.isfile(filepath) # returns True if the filepath is a file
os.path.isdir(filepath) # returns True if the filepath is a folder (directory)
If you want to read more, you can find some helpful documentation here
File Search #
💻 In file_search.py finish the code for find_file().
- Parameters:
- folder (string): filepath of the folder to search
- target (string): name of the file to find
- If it finds the
targetfile, it should print out the entire filepath
Example usage:
find_file(desktop_path, "file_search.py")
/Users/bgenzlinger/Desktop/dpcs/unit01_cryptography/lab_recursive_drawing/file_search.py
Print Python Files #
💻 In file_search.py finish the code for print_python_files().
- Parameter:
- folder (string): filepath of the folder to search
- Any time it finds a
.pyfile, it should print out the entire filepath. - You may use the
inkeyword to check membership.
Example Usage:
find_file(desktop_path)
spotify_export.py
export_whatsapp.py
whatsapp_df.py
class_planner.py
selection_sort.py
[2] Fractal Drawing #
A fractal is a geometric pattern which is self-similar in some way. These patterns often look similar at different scales, no matter how much you zoom in or out. Fractals can be found throughout nature (snowflakes, ferns, riverbeds, circulatory systems, etc.) One popular example of fractal geometry is the Sierpinsky Triangle
Sierpinsky Triangle #

The sierpinsky triangle is created by repeating one basic rule:
Every time you draw a triangle, draw 3 smaller triangles inside it instead.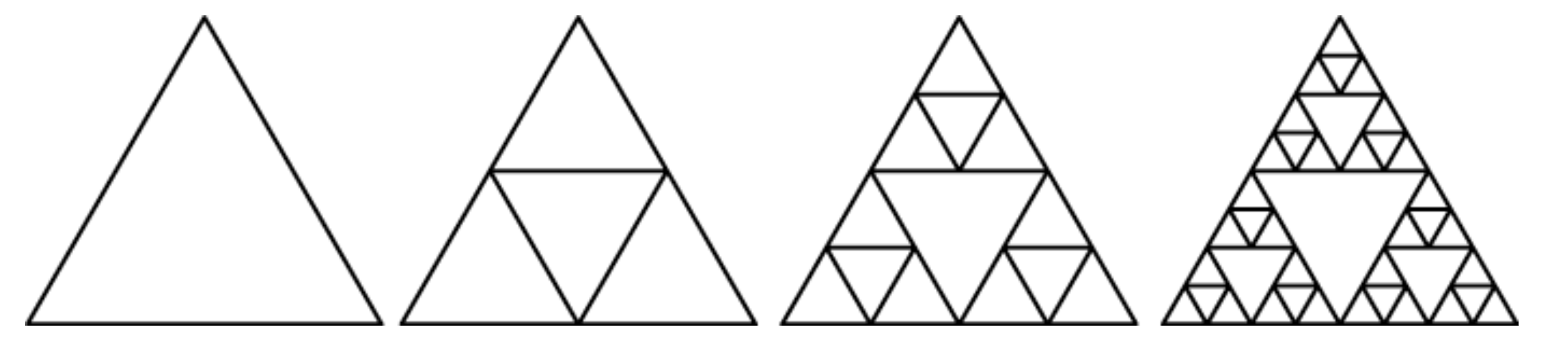
The points of the smaller triangles are located at the midpoints of the larger triange’s side.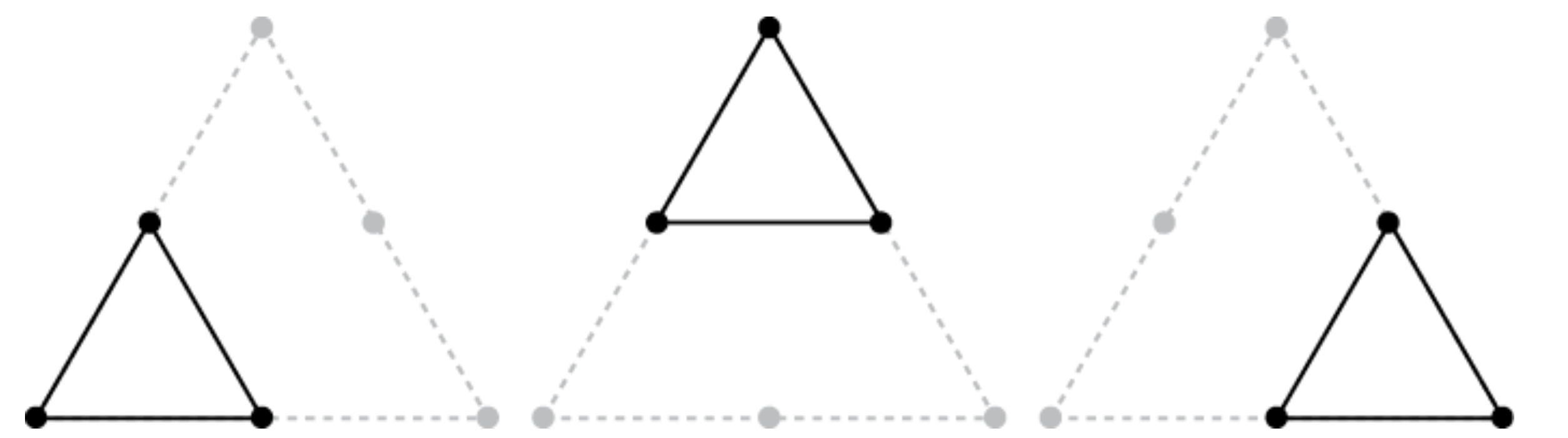
💻 In sierpinsky_triangle.py, code the recursive function sierpinsky() to draw the triangle pattern.
- Parameters:
- size (int): side length
- loc (turtle.Vec2D): location of the bottom left corner
- Base case: when the size gets below a certain number (you choose) just draw a normal triangle using the provided
triangle()function
Helpful Turtle Functions
# locations
my_location = turtle.pos() # get the turtle's current position
# moving the turtle
turtle.forward() # go forward a certain amount
turtle.backward() # go backward a certain amount
turtle.goto(my_location) # go to a previously stored position
# changing direction
turtle.right(60) # turn right a certain amount (angle)
turtle.left(60) # turn right a certain amount (angle)
turtle.setheading(0) # set the turtle due east
turtle.setheading(90) # set the turtle due north
turtle.setheading(180) # set the turtle due west
turtle.setheading(270) # set the turtle due south
[3] Deliverables #
⚡✨ Once you complete the lab, be sure to complete these two steps:✏️ Go to your Syllabus Content Checklist in your Google Drive and update it accordingly.
💻 Push your work to Github
- git status
- git add -A
- git status
- git commit -m "describe your code here"
- git push
- git remote